You'll be connected to the convention center at The Star Grand at The Star Gold Coast, and within a 30-minute stroll of Pacific Fair Shopping Centre and Surfers Paradise Beach. Highlights at this luxury hotel include 8 restaurants, 6 bars/lounges, and a casino. Check out the latest range of accommodation deals offered at The Star Gold Coast! ACCOMMODATION DEALS & PACKAGES. Current specials. Star casino gold coast accommodation specials. The Star Gold Coast offers luxurious hotel accommodation, a world-class 24-hour casino, sumptuous restaurant dining, lively bars, and thrilling entertainment! Book a Stay & Dine hotel package and save 25% 1 on luxury accommodation at The Star Grand Gold Coast with a $100 daily dining credit 2 included. Search for the cheapest hotel deal for The Star Grand at The Star Gold Coast in Broadbeach. KAYAK searches hundreds of travel sites to help you find and book the hotel deal at The Star Grand at The Star Gold Coast that suits you best. $187 per night (Latest starting price for this hotel).
Importance of Blackjack Variances
For blackjack and its variants (e.g. Blackjack Switch, Spanish 21), the true count also serves a strategic purpose: the AP has mid-hand decisions to make (stand, hit, double, split, surrender) that vary based on the true count. For example, in blackjack: With a high true count (larger bet), the AP will adjust his play from basic strategy. Playing Deviations are times when the true count dictates a decision that differs from Basic Strategy. Basic Strategy is the default correct playing decision for every possible hand combination in Blackjack. But as the Running and True Counts change, there are times that the ג€ correctג€ play also changes. Here's the situation: You're playing in a multiple deck game, and receive a five and a three for a two-card total of eight while the dealer flips a six as his upcard. Standing with this hand is, of.
The importance of blackjack variances and a proper understanding of variance in gambling cannot be underestimated. Blackjack players can come to think they 'know how to beat blackjack' if they go on a lucky streak, or they might come to think that blackjack isn't their game if they have a high negative variance in the early rounds of their blackjack playing. So given how important variances are to your expectations in blackjack, I'll try to explain what blackjack variance is and why it's important to keep in mind when analyzing your blackjack results.
So what are blackjack variances? To answer that question, I'll need to define a few blackjack terms -- so please bear with me.
Payout Percentages and the House Edge
The short answer is that blackjack variances are the deviations from expected payback in blackjack. 'Expected payout' is the amount of money (as a percentage) that you might expect to win back when betting on blackjack. It is closely tied to the house edge. The house edge exists so the casino stays in business, because casino games are typically weighted in the favor of the casino and against the player. The house edge in blackjack for a player using 'perfect' or optimal basic strategy is only around 0.5%, which means your expected payout will be around 99.5%.
This makes blackjack actually one of the best games in the casino. So for every $100 you bet at the blackjack table, you can expect to win back $99.50. You'll only lose $0.50 on every hundred dollars you spend (if you play perfect strategy, which all new players won't). For those managing expectations, though, the low house edge makes blackjack variances more subtle and more difficult to analyze, at least when you're going with your 'gut' or gamblers instinct.
Variances in Wins and Losses

That's because your expected payout or expectation is only an average. It's a theoretical expecation, and one not likely to occur too many times in your blackjack sessions. Sometimes you'll lose a whole lot more than $0.50 per $100 bet. You might lose $50.00 on a hundred dollar bet, if the cards aren't hitting right. On the other hand, you'll sometimes walk away from the table with more than you started out. You wouldn't play the game if you never won. So you'll win sometimes, but to account for the winning opportunities, you'll lose more than expected at other times. Losing more than you're expected to lose is a variance from your payback expectations, while winning your bets is also a variance from those expectations. Therefore, the amount your blackjack session deviates from expectation is the variance.
Blackjack Deviations
Your results will vary each time you bet on blackjack. Most of the time when playing blackjack, your results will vary widely, from large losses to large wins. Seldom will a player with a 99.5% expectation actually walk away with 99.5% of the money he or she bet. Expectation involves the odds about what you can expect to win or lose over a long period of time. Actually, it's over an infinite number of blackjack hands, because the possibility always exists that you'll just keep winning more than expected or losing more than expected.
This kind of deviation can fool a player at the blackjack table. If you're not a serious player, but just having fun, you might get the sensation you're having good luck or bad luck. You'll get the feeling you're getting lucky and that's that. Where the problem comes in is when you are a professional or serious amateur blackjack player, and you are trying out some new blackjack tips, recently learned blackjack strategy or card counting techniques. Because even really long sessions of blackjack are just a small sampling of the possibilities. Six months of blackjack sessions aren't a tiny sample, when compared to the idea that the expectation is based on a theoretical infinite number of hands. So you're not getting a full picture (or even a half-full picture) about whether your new blackjack method is working. You may just be riding the highs or lows of the blackjack variances.
So the importance of blackjack variances is they can fool us into false assumptions about our blackjack playing. Maybe you'll come away thinking you have learned how to beat blackjack, or you're a much better player than you really are. Or maybe you're doing all the right things, but the cards aren't falling your way. Players need to understand the nature of blackjack variances, then, and learn to analyze their game based not entirely on results, but on the soundness of the strategy being employed. You can make all the right moves and lose, and you can make all the wrong moves and win. That's the essence of blackjack variances. Sometimes you beat the odds.
Standard Deviation
To get an idea about our real expectations when playing blackjack, consider the standard deviation. This will give you some idea of the kind of blackjack variances you can expect. It's pretty interesting, because it shows how small the gambling margins can be in the short term, even though in the long term, blackjack is a negative expectation game.
You can figure what is called a 'standard deviation'. You might remember this from grade school, where you get an average of a group of numbers, then calculate the standard deviation from that number. In calculating a blackjack standard deviation with a computer software program, though, you won't be testing a select group of five or ten numbers. You'll be testing well over a million deviations.
The standard deviation in blackjack is simply calculating the probabilities you will win or lose and extracting your odds from that. That is, the standard deviation can tell you your odds of winning, losing or pushing when playing blackjack. Without getting too far into the numbers, at least one gambling math expert has figured there are over 723,000,000 (yes, that's 723 million) card combination scenarios where you walk away from the table a winner. But there are over 836,000,000 combinations where you walk away a loser. And there are only a paltry 144,000,000 potential cases where you walk away with the same money you started with or 'push'.
Considering all these numbers as percentages of 100%, the standard deviation will tell you that your chances of walking away a net winner in blackjack is around 42.42% of the time, rounded up. Your odds of walking away from the blackjack table a loser are around 49.10%, rounded up. Your odds of walking away with a push is somewhere around 8.47% of the time.
If you want to read more about the numbers behind blackjack variances and standard deviation, visit the blackjack variance page on the Wizard of Odds website. The Wizard of Odds has run statistical breakdowns of the odds on virtually every major game you'll find in a casino.
Negative Expectation, But With Hope
So blackjack is a negative expectation game. There's a house edge that says you will lose in the long run, if you play an infinite number of hands. But in the short term, you'll walk away a winner 42% of the time. In fact, you'll walk away not losing nearly 51% of the time. And over 91% of the time, you'll experience a variance from the expected payouts in blackjack. Blackjack variances will happen 9 out of 10 times you walk up to the blackjack table. You need to keep this in mind when playing blackjack and analyzing your results.
- Appendices
- Miscellaneous
- External Links
Blackjack Deviations Drills
On This Page
Introduction
Blackjack Deviations From Basic Strategy
Common questions for novice players: What is single deck blackjack? Is it better to play single deck blackjack versus multi-deck variations? To use the basic strategy, look up your hand along the left vertical edge and the dealer's up card along the top. In both cases, an A stands for ace. From top to bottom are the hard totals, soft totals, and splittable hands. For specific tips, we present two charts depending on whether the dealer hits or stands on soft 17.
Other basic strategy rules: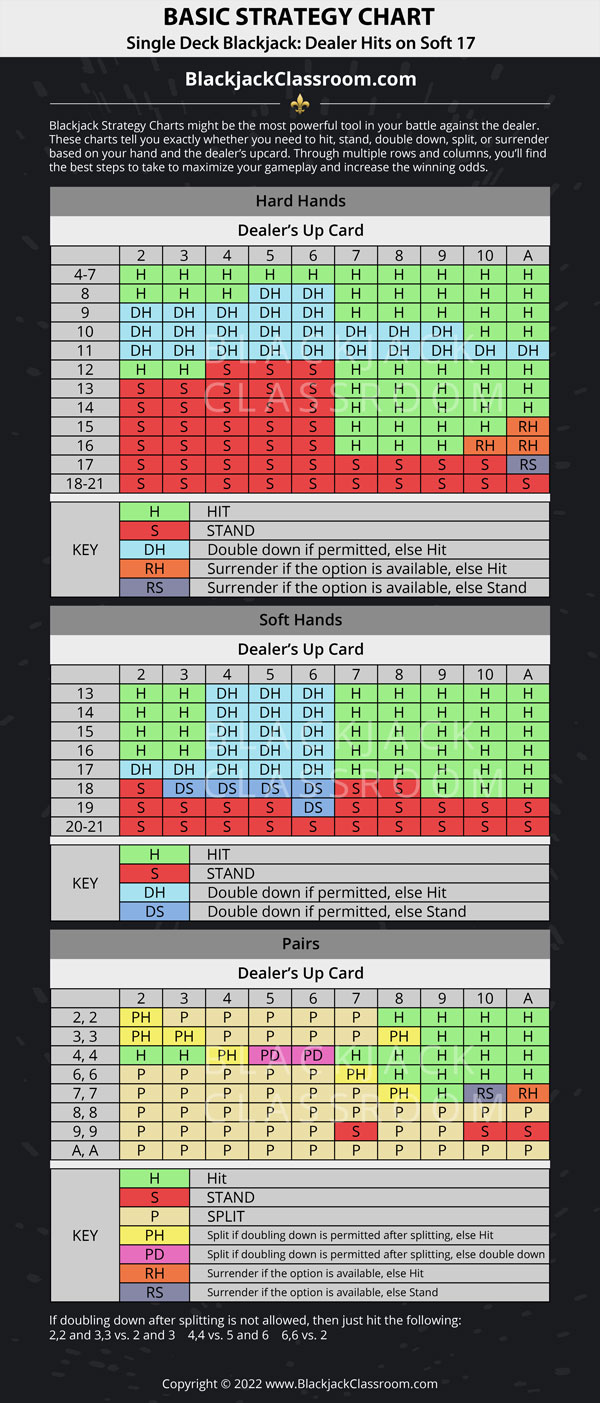
That's because your expected payout or expectation is only an average. It's a theoretical expecation, and one not likely to occur too many times in your blackjack sessions. Sometimes you'll lose a whole lot more than $0.50 per $100 bet. You might lose $50.00 on a hundred dollar bet, if the cards aren't hitting right. On the other hand, you'll sometimes walk away from the table with more than you started out. You wouldn't play the game if you never won. So you'll win sometimes, but to account for the winning opportunities, you'll lose more than expected at other times. Losing more than you're expected to lose is a variance from your payback expectations, while winning your bets is also a variance from those expectations. Therefore, the amount your blackjack session deviates from expectation is the variance.
Blackjack Deviations
Your results will vary each time you bet on blackjack. Most of the time when playing blackjack, your results will vary widely, from large losses to large wins. Seldom will a player with a 99.5% expectation actually walk away with 99.5% of the money he or she bet. Expectation involves the odds about what you can expect to win or lose over a long period of time. Actually, it's over an infinite number of blackjack hands, because the possibility always exists that you'll just keep winning more than expected or losing more than expected.
This kind of deviation can fool a player at the blackjack table. If you're not a serious player, but just having fun, you might get the sensation you're having good luck or bad luck. You'll get the feeling you're getting lucky and that's that. Where the problem comes in is when you are a professional or serious amateur blackjack player, and you are trying out some new blackjack tips, recently learned blackjack strategy or card counting techniques. Because even really long sessions of blackjack are just a small sampling of the possibilities. Six months of blackjack sessions aren't a tiny sample, when compared to the idea that the expectation is based on a theoretical infinite number of hands. So you're not getting a full picture (or even a half-full picture) about whether your new blackjack method is working. You may just be riding the highs or lows of the blackjack variances.
So the importance of blackjack variances is they can fool us into false assumptions about our blackjack playing. Maybe you'll come away thinking you have learned how to beat blackjack, or you're a much better player than you really are. Or maybe you're doing all the right things, but the cards aren't falling your way. Players need to understand the nature of blackjack variances, then, and learn to analyze their game based not entirely on results, but on the soundness of the strategy being employed. You can make all the right moves and lose, and you can make all the wrong moves and win. That's the essence of blackjack variances. Sometimes you beat the odds.
Standard Deviation
To get an idea about our real expectations when playing blackjack, consider the standard deviation. This will give you some idea of the kind of blackjack variances you can expect. It's pretty interesting, because it shows how small the gambling margins can be in the short term, even though in the long term, blackjack is a negative expectation game.
You can figure what is called a 'standard deviation'. You might remember this from grade school, where you get an average of a group of numbers, then calculate the standard deviation from that number. In calculating a blackjack standard deviation with a computer software program, though, you won't be testing a select group of five or ten numbers. You'll be testing well over a million deviations.
The standard deviation in blackjack is simply calculating the probabilities you will win or lose and extracting your odds from that. That is, the standard deviation can tell you your odds of winning, losing or pushing when playing blackjack. Without getting too far into the numbers, at least one gambling math expert has figured there are over 723,000,000 (yes, that's 723 million) card combination scenarios where you walk away from the table a winner. But there are over 836,000,000 combinations where you walk away a loser. And there are only a paltry 144,000,000 potential cases where you walk away with the same money you started with or 'push'.
Considering all these numbers as percentages of 100%, the standard deviation will tell you that your chances of walking away a net winner in blackjack is around 42.42% of the time, rounded up. Your odds of walking away from the blackjack table a loser are around 49.10%, rounded up. Your odds of walking away with a push is somewhere around 8.47% of the time.
If you want to read more about the numbers behind blackjack variances and standard deviation, visit the blackjack variance page on the Wizard of Odds website. The Wizard of Odds has run statistical breakdowns of the odds on virtually every major game you'll find in a casino.
Negative Expectation, But With Hope
So blackjack is a negative expectation game. There's a house edge that says you will lose in the long run, if you play an infinite number of hands. But in the short term, you'll walk away a winner 42% of the time. In fact, you'll walk away not losing nearly 51% of the time. And over 91% of the time, you'll experience a variance from the expected payouts in blackjack. Blackjack variances will happen 9 out of 10 times you walk up to the blackjack table. You need to keep this in mind when playing blackjack and analyzing your results.
- Appendices
- Miscellaneous
- External Links
Blackjack Deviations Drills
On This Page
Introduction
Blackjack Deviations From Basic Strategy
Common questions for novice players: What is single deck blackjack? Is it better to play single deck blackjack versus multi-deck variations? To use the basic strategy, look up your hand along the left vertical edge and the dealer's up card along the top. In both cases, an A stands for ace. From top to bottom are the hard totals, soft totals, and splittable hands. For specific tips, we present two charts depending on whether the dealer hits or stands on soft 17.
Other basic strategy rules:Blackjack Deviations Chart
- Never take insurance or 'even money.' The house edge on insurance is 5.9%, based on one deck.
- If there is no row for splitting (fives and tens), then look up your hand as a hard total (10 or 20).
- If you can't split because of a limit on re-splitting, then look up your hand as a hard total, except aces. In the extremely unlikely event you have a pair of aces you can't re-split and drawing to split aces is allowed, then double against a 5 or 6, otherwise hit.
Internal Links
Blackjack main page.
Blackjack Appendix 3A lists exceptions to the single deck, dealer stands on soft 17, basic strategy based on the exact composition of the player's hand.
Blackjack Appendix 3C lists exceptions to the single deck, dealer hits on soft 17, basic strategy based on the exact composition of the player's hand.
Boss Media Appendix 1 has a composition dependent basic strategy for single-deck, dealer stands on soft 17, blackjack.
Written by:Michael Shackleford
